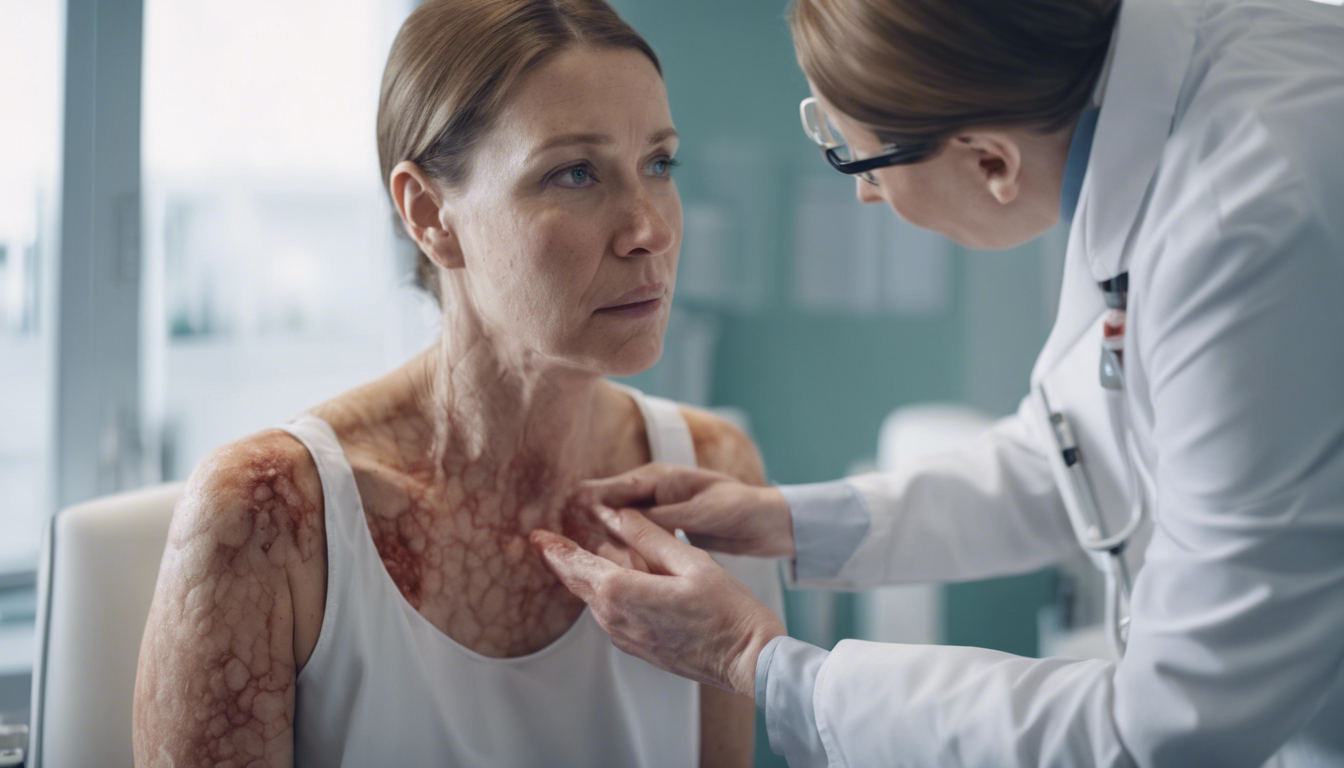
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by itchy, red, swollen, and cracked skin. The itchiness can be severe, often disturbing sleep and daily activities. Although it predominantly affects children, it can persist or start in adulthood, significantly impacting life quality.
The disease’s etiology is complex, involving genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. Skin barrier dysfunction allows allergens and microbes to enter, prompting an immune response that leads to skin inflammation. This inflammation is not only uncomfortable but can also be visibly distressing, with societal stigma sometimes exacerbating the psychological burden.
Globally, atopic dermatitis affects approximately 230 million people, with its prevalence varying by region. The disease is more common in urban areas and developed countries, presumably due to lifestyle factors that include reduced exposure to diverse microorganisms during childhood, which could prevent proper immune system development.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis can range from mild to severe and often flare up or recede sporadically. Typical symptoms include dry skin, itching, red or brownish-gray patches, small raised bumps, which may leak fluid and crust over when scratched, thickened skin, and raw, sensitive skin from scratching. The pattern and severity of symptoms can vary widely from person to person.
Treatment for atopic dermatitis aims to alleviate symptoms and prevent new flare-ups. Standard therapies include topical treatments like corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and creams to repair the skin barrier. Antihistamines may be used to decrease severe itching while antibiotics are prescribed if bacterial skin infections occur.
For female patients, hormonal fluctuations can complicate atopic dermatitis. Women may experience worsening symptoms during particular periods such as puberty, menstruation, or pregnancy. Furthermore, some treatment options might not be suitable during pregnancy or breastfeeding, requiring careful management by healthcare providers.
New research is actively exploring novel treatments for atopic dermatitis. These include biologics, which target specific parts of the immune system. Dupilumab, the first biologic approved for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis, has shown promise in improving skin health and reducing the need for topical steroids.
Furthermore, recent advances in microbiome research indicate that the application of beneficial bacteria directly to the skin might help treat or even prevent atopic dermatitis by strengthening the skin barrier and reducing bacterial infections, one of the common complications of the disease.
Looking ahead, several experimental therapies are in development. These include Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, which modulate the immune response, and phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitors, designed to reduce inflammation. Clinical trials are ongoing, and these treatments could offer new hope for patients with severe cases who do not respond well to traditional therapies.
The quest to understand and treat atopic dermatitis continues, reflecting the complexities of the disease and the diverse needs of those it affects. It remains an area of active research with a strong focus on improving the quality of life for patients, particularly those with unique challenges such as women affected by hormonal variations. Advocacy and patient-centered care play crucial roles in managing this chronic condition effectively.
You may also like
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis: Symptoms, Treatments, and Innovation
This article delves into the chronic skin condition known as atopic dermatitis, focusing on its symptoms, treatments, and particularly its impact on males. It also explores recent studies and experimental treatments, providing insights into the geographical prevalence and its various manifestations.
Hair Loss Treatments and Skin Diseases
Hair loss is a global issue affecting millions of men and women worldwide, with distinct patterns and causes between genders. This article delves into current treatments and explores emerging technologies and research in combating hair loss. Additionally, it examines associated skin conditions, including acne, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and dental care, outlining the latest in treatment advancements.
Acne: Symptoms, Treatments and Advances in Research
Acne is a common skin condition that affects teenagers and adults worldwide, presenting unique challenges for each group. This article delves into the symptoms and available treatments for acne, alongside exploring emerging studies and innovative approaches in combating this condition. Additionally, it provides insight into related dermatological issues such as hair loss, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and advancements in dental care.
Atopic Dermatitis: Symptoms, Treatments and Promising New Research
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation and itchiness. This article explores the symptoms and treatments for atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, offering insights into innovative treatments and ongoing research for these skin conditions.
Dental Implants and Oral Hygiene: Revolutionary Treatments
This comprehensive article delves into the domain of dental implants and oral hygiene, providing insights into various treatment methods, geographical incidence, and groundbreaking studies on the horizon. Additionally, it explores related health issues such as hair loss, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and acne, offering a glimpse into innovative treatments that promise to transform care standards.