Operating system guide
Features of the operating system
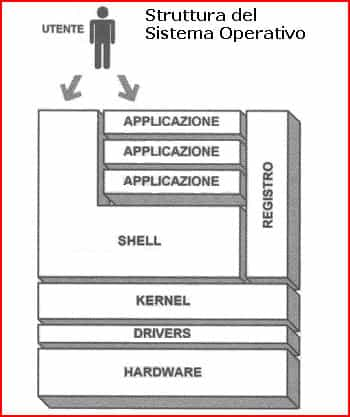
Operating system, or system software, set of programs in a computer that controls the execution of user programs and the use of the hardware resources they use, acting as an interface between the hardware and the user who uses it. The operating system acts both as a supervisor for all the other programs that run on the computer and as a manager of resources, such as processors, external mass storage media, working memory, input/output peripherals, etc. The role is more evident in multi-user systems in which machine resources (memories, peripherals, etc.) are shared by multiple programs and generally dynamically allocated. Being closely linked to the physical structure of the computer, operating systems are characteristic of different types of computers and are not interchangeable. An operating system generally also has a certain number of utility programs (for resource tuning, archive sorting, etc.) that play a collateral role and come into operation upon user request. The main programs of the operating system. The supervisor, or monitor, is the main part of the operating system; its fundamental task is the management of the computer hardware. The dispatcher, or dispatcher, is a program that is called by the supervisor when it is necessary to decide which of the processes resident in memory waiting for processing should be assigned the next time interval of the CPU (central processing unit). Memory management according to appropriate techniques is the task of the memory distributor program which is recalled at the appropriate time by the supervisor. The choice of the job to be performed among those unexpected to move into the operational phase is made according to specific priority criteria by the scheduler, which also manages the resources in the various types of memory. The interpreter, or interpreter, carries out the analysis and interpretation of the requests made by the user in the characteristic language of the computer. The logical input/output is made up of a series of programs that allow access to the archives recorded on mass memories or on other external media: to carry out operations on the peripheral units the logical input/output uses another system of programs called physical input/output.
Main operating systems
- AcornOS
- AmigaOS
- AROS
- BeOS
- Haiku
- Zeta
- CP/67
- CP/CMS
- CP/M
- DOS
- DR-DOS
- DOS/VS
- DOS/VSE
- FreeDOS
- MS-DOS
- PC-DOS
- GEOS
- GNU/Linux
- ALT Linux
- ArchLinux
- CentOS
- Damn Small Linux
- Debian GNU/Linux
- Dyne:bolic
- Fedora Core
- Fox Desktop
- Gentoo Linux
- Knoppix
- Kororaa
- Mandriva Linux, known as "Mandrake Linux" until 2004
- MEPIS
- Pardus
- PuppyLinux
- Red Hat Linux
- Rxart
- Slackware (also in the (live) derivative Slax)
- Slamd 64
- I know.Of.Linux
- SUSE Linux
- Ubuntu Linux (also in the Xubuntu, Kubuntu, Edubuntu, Ubuntu Lite variants)
- GNU/Hurd
- MacOS
- Menuet OS
- MorphOS
- MSX-DOS
- MVS
- OS/2
- OS/400 now I5/OS
- OS/360
- QNX
- POSIX
- TOS
- Unix
- AIX
- BSD (pure)
- FreeBSD
- DragonFlyBSD
- FreeBSD
- Minix
- NetBSD
- OpenBSD
- NetBSD
- OSF/1
- Tru64
- BSD (Improper Derivatives)
- SunOS
- NEXTSTEP
- Mac OS
- System III and System V
- Solaris
- AIX
- HP-UX
- IRIX
- VM/CMS
- VM/ESA
- VM/SP
- VM/XA
- z/VM
- VMS
- OpenVMS
- Windows
- 16/32-bit graphical environments for MS-DOS operating systems:
- Windows 3.0
- Windows 3.1
- Windows 3.11 (Windows for Workgroups)
- 32-bit Windows operating systems
- Windows 95
- Windows 98
- Windows ME
- 32-bit Windows operating systems on NT technology
- Windows NT 3.x (client and server versions)
- Windows NT 4 (client and server versions)
- Windows 2000 (client and server versions)
- Windows XP (client version), Windows Server 2003 (server version), and Windows XP x64 Edition (64-bit version)
- Windows Vista (client version), Windows Longhorn Server (server version, under development)
- 16/32-bit graphical environments for MS-DOS operating systems:
- ReactOS (open-source clone with NT architecture)
You may also like
Home Cleaning: A Glimpse into the Future of Floor-Cleaning Robots in 2025
In 2025, the world of floor-cleaning robots will witness significant innovations and market shifts. From advanced models to competitive deals, this comprehensive exploration examines emerging technologies, geographic trends, and purchasing advice to help consumers make informed decisions in acquiring their ideal floor-cleaning robot.
Electric Razors: Innovations and Market Trends
As we step into 2025, the electric razor market is brimming with innovations that promise to transform personal grooming. This article delves into the latest models, market trends, and emerging technologies in the electric razor industry. Explore the best offers available and understand the regional buying trends shaping the future of personal grooming.
Electric Toothbrushes: Technologies and best deals
Electric toothbrushes have become a staple in oral hygiene routines, thanks to innovations, affordability, and market trends influencing global consumer choices. This article delves into the latest models, technologies, best deals, and geographical trends shaping the choice of electric toothbrushes today.
All-Season Motorcycle Tires in 2025
The year 2025 marks a pivotal moment for all-season motorcycle tires, with new models featuring cutting-edge technology, competitive pricing, and robust market trends. This comprehensive analysis explores advancements, regional market impacts, and exciting offers in the all-season motorcycle tire sector.